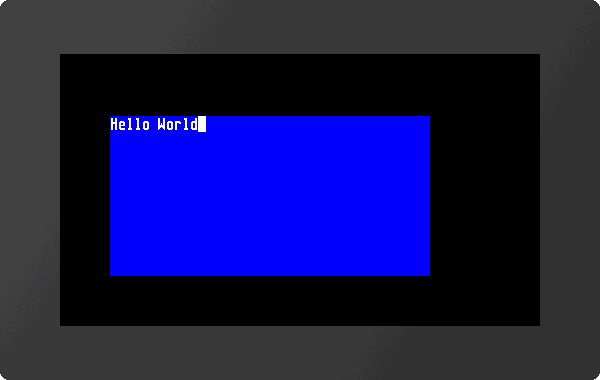
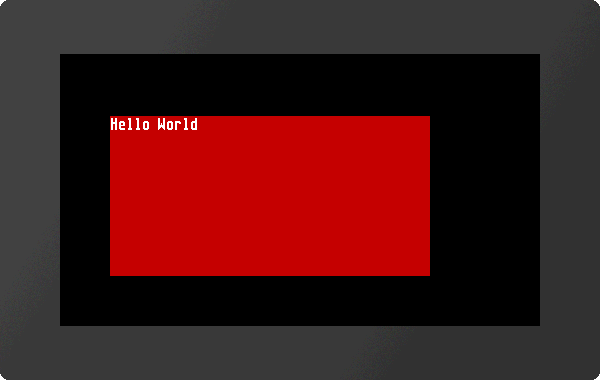
Terminal window #Y
The terminal window is useful for quick test of serial interface connection; for that put the pin DPROT to GND (switch off the protocol) and then power-up the display. All data received from serial interface are displayed directly (ASCII codes and CR/LF). FF clears the terminal window and set the cursor position to home position.
The terminal window provides also an easy way for simple outputs and error messages during development.
Terminal window settings
Size and position settings (Terminal Define Window) |
x(0), y(0), Anchor(7), Columns(x-DisplayResolution/8), Rows(y-DisplayResolution/16) |
|
Color settings (Terminal Define Color) |
Text-Color, Text-Opacity(100), Background-Color($000000), Background-Opacity(0) |
|
Drawing order (Layer) (Terminal Define Layer) |
Layer |
|
Terminal window on/off (Terminal Define Output) |
Output, Visibility(=Output) |
|
Cursor on/off (Terminal Cursor Blink) |
Cursor |
|
Set cursor position (Terminal Cursor Position) |
Column, Row(no change) |
|
Save cursor position (Terminal Cursor Save) |
||
Restore cursor position (Terminal Cursor Restore) |
Terminal window output
Print string (Terminal Print Ascii) |
String |
|
Print formatted string (Terminal Print Formated) |
"Formatted string"; Value1, Value2, ..., ValueN |
|
Print date/time (Terminal Print Date) |
"Dateformat"; date (act. time); 1/100sec |
|
Print module information (Terminal Print Info) |
||
Print firmware version string (Terminal Print Version) |
Terminal window settings
All important settings of the terminal window are summarized in this command group.
#YDW |
x(0), y(0), Anchor(7), Columns(x-DisplayResolution/8), Rows(y-DisplayResolution/16) |
The command defines the dimensions of the terminal window. The width results from the specification of the columns and rows and the font size (8x16): Width in pixels = 8 ∗ columns; Height in pixels = 16 ∗ lines
|
... #YDW 50,50,7,40,10 ... |
#YDC |
Text-Color, Text-Opacity(100), Background-Color($000000), Background-Opacity(0) |
The command sets the color and opacity of the font and the background. The color is transferred as a 24-bit RGB value (e.g. $c80000, %110010000000000000000000, (RGB(200,0,0))).
|
... #YDC $ffffff,100,$c80000 ... |
#YDL |
Layer |
The command sets the drawing order (Layer) of the terminal window:
Layer |
|
0 |
Terminal window is shown behind all objects |
1 |
Terminal window is shown on top |
By default, the terminal is always on top.
|
... #YDL 0 ... |
#YDO |
Output, Visibility(=Output) |
With this command the terminal window output can be activated or deactivated and the visibility can be set. If only one parameter is passed, it applies to both values.
Definition of the Output:
Output |
|
0 |
Terminal window output is deactivated |
1 |
Terminal window output is activated |
Definition of the Visibility:
Visibility |
|
0 |
Terminal is invisible |
1 |
Terminal is visible |
#YDO 0 |
Outputs are disabled and the terminal is invisible |
#YDO 1 |
Outputs are activated and the terminal is visible |
#YDO 0,1 |
Outputs are deactivated and the terminal is visible |
#YDO 1,0 |
Outputs are activated and the terminal is invisible. |
#YCB |
Cursor |
The command sets the visibility of the Cursor:
Cursor |
|
0 |
Cursor is invisible |
1 |
Cursor is visible |
#YCP |
Column, Row(no change) |
The command sets the cursor position within the terminal window. If no line is specified, it is not changed. The position starts at (1,1).
|
... #YCP 10,2 ... |
#YCS |
|
The current position of the cursor is saved.
#YCR |
|
The cursor is placed on the last saved position.
Terminal window output
This group includes commands to display strings and predefined outputs on the terminal window.
#YPA |
String |
The characters (strings) are displayed in the terminal window. Entire character strings (e.g. "Test", 'Test') or individual ASCI characters ($21, 33, ?!) can be transferred. The semicolon forms the end of the string.
|
... #YPA "Hello World"$21; ... |
#YPF |
"Formatted string"; Value1, Value2, ..., ValueN |
The formatted string is displayed on the terminal window. If the variable set repeats, the format string is used again. The structure is explained in more detail in the section Formatted string.
|
... #YPF "Formatstring %d"; 42 ... |
#YPD |
"Dateformat"; date (act. time); 1/100sec |
The date and time are displayed on the terminal window. The way of presentation is based on the date format. The structure is explained in more detail in the section Date formats.
|
... #YPD "%D.%M.%Y"; ... |
#YPI |
|
Module parameters (e.g. firmware version, resolution, or interface parameters) are displayed in the terminal window.
#YPV |
|
The firmware version of the module is displayed in the terminal window.